-
Sustainable binder alternative - 18/12/2023
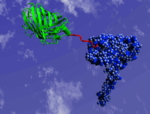
Plastic is all around us; and unfortunately, it is not going away any time soon. The search for more sustainable solutions is fully underway. However, binders that degrade only with difficulty or not at all are still used to bond natural materials such as wood and straw - not yet truly environmentally friendly. Fraunhofer researchers are working on an insect-inspired wood binder that makes bonded wood products both resistant and biodegradable.
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/news/copied-insects-new-biological-wood-binder-under-development
-
Microorganisms degrade biobased turf infill - 17/10/2023

There are thousands of artificial turf pitches in Germany. They are extremely practical, but often not at all environmentally friendly. When it rains or the pitch is used, plastic particles from the rubber granules can be released into the envronment, where they remain. Researchers at the University of Stuttgart along with the company TECNARO are now developing an artificial turf with an infill that biodegrades as soon as it leaves the pitch.
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/news/eco-friendly-artificial-turf-sports-pitch-s-good-people-and-environment
-
-
-
-
Project BW2Pro - 29/08/2022

In 2020, Germany’s population collected over 5 million tonnes of biowaste. Most of this was composted, and some was fermented into biogas. Scientists in Baden-Württemberg think there's room for more. Within the project ‘Biowaste to Products’ (BW2Pro) they want to transform biowaste into new products in a biorefinery. The idea is to produce biodegradable plant pots, mulch material, fertilisers, enzymes and biobased plastics in addition to…
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/news/biowaste-products-biorefinery-transforms-biowaste-new-products
-
Press release - 13/01/2022
Making important raw materials for fine chemicals out of carbon dioxide really works. As part of the Max Planck collaborative project eBioCO2n, a team of researchers from Fraunhofer IGB have successfully performed a first ever fixation of CO2 via a multi-enzyme enzyme reaction driven by electricity yielding a prospective intermediate for the chemical industry. The process for electro-biocatalytic CO2 fixation was recently published and is…
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/pm/turning-harmful-co2-useful-chemicals
-
Climate-friendly circular economy - 11/11/2021

A Fraunhofer team has successfully produced a dye using CO2 adsorbed from the air. The aim is to move towards a climate- and resource-friendly circular economy. Chemicals, as well as fuels, can be produced cost-effectively using this process. How does the technical process work, and what opportunities does it open up?
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/news/co2-air-raw-material-chemicals
-
Press release - 02/08/2021
Carbon dioxide is one of the main drivers of climate change – which means that we need to reduce CO2 emissions in the future. Fraunhofer researchers are highlighting a possible way to lower these emissions: They use the greenhouse gas as a raw material, for instance to produce plastics. To do this, they first produce methanol and formic acid from CO2, which they convert via microorganisms into building blocks for polymers and the like.
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/pm/co2-raw-material-plastics-and-other-products
-
-
Article - 30/01/2019

Industry has been using enzymes for over a hundred years. While it initially had to content itself with natural enzymes, it is now increasingly possible to design tailor-made biocatalysts with specific properties. The start-up company candidum GmbH from Stuttgart promises to achieve this faster than ever before - mostly thanks to accelerated virtual screening.
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/news/candidum-computer-assisted-enzyme-design
-
Dossier - 20/03/2017

Petroleum is the raw material for basic chemicals. Growing demand and dwindling resources mean that the chemical industry is increasingly focusing on renewable resources. Lignin is a wood component that is proving to be a promising resource. It is currently almost exclusively used for generating energy, although it could also be used for other purposes. In Baden-Württemberg, a research consortium is specifically focused on exploring its…
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/dossiers/lignin-a-natural-resource-with-huge-potential
-
Dossier - 16/06/2014

Biotechnology opens up numerous opportunities for the food industry. The targeted use of biotechnological methods can help reduce the quantity and number of unhealthy ingredients in foods as well as degrade allergenic substances. Genomic research and targeted breeding also greatly facilitate progress in agriculture. Food biotechnology therefore contributes significantly to saving resources, optimising harvest yields and producing better foods.
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/dossiers/biotechnology-as-a-tool-for-the-production-of-food
-
-
-
-
Dossier - 23/07/2012

Extremophilic bacteria love it hot, sour or salty, toxic substances like heavy metals also do them good and even give them energy. As molecular and systems biology techniques get better and better, industry is also becoming increasingly interested in these exotic organisms. What potential does knowing the biochemistry of extremophilic bacteria have for the pharmaceutical, cosmetics and sanitary articles industries?
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/dossiers/extremophilic-bacteria
Website address: https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/search