Biocatalytic foams enable the sustainable synthesis of complex molecules
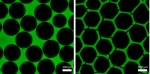
Conventional chemical synthesis processes consume large amounts of energy and environmentally harmful solvents. Prof. Dr. Christof Niemeyer’s team at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology has generated porous, solid foams from crosslinked enzymes that allow the production of high-quality compounds under significantly more environmentally friendly conditions. The novel biocatalysts are also extremely resistant and have a long shelf life.