-
-
-
Press release - 30/03/2023
Composite materials provide stability in aircraft parts, sports equipment, and everyday household items. However, most of these materials have a poor carbon footprint and are not naturally degradable. A more sustainable alternative has been developed by a team from the University of Stuttgart. This completely bio-based composite material is made of flax fibers and the biopolymer chitosan.
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/pm/green-composite-material-made-flax-and-chitosan
-
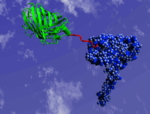
Diatoms as a biorefinery - 05/05/2023
Renewable raw materials that can be used as alternatives to fossil resources already exist. However, to turn them into everyday products, plant oils and other renewable raw materials not only have to be extracted, but often have to undergo complex chemical processing. Researchers at the University of Konstanz have now converted microalgae cells into tiny refineries to produce and upgrade raw materials, creating a supply of sustainable chemicals.
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/news/microalgae-sustainable-chemical-production-mini-factory
-
-
3D-Thermocell project - 17/05/2023

Replacing plastic – for example in packaging – is not that easy but nevertheless urgently needed. In the 3D-Thermocell project, researchers at DHBW Karlsruhe are currently developing new plastic substitute products made of thermoformable paper as a renewable resource, which should be cheap and light and easy to dispose of along with waste paper. The characterisation and application of demonstration models will start soon.
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/paper-instead-plastic-sustainable-packaging-good-conscience
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Press release - 30/08/2023
Rising sea levels due to climate change and artificial irrigation cause soil salinity to increase. This has a negative impact on agriculture, including viticulture. The plants die, yields decrease. Researchers of Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) have therefore studied a wild grapevine of higher salt tolerance. Their goal is to identify the genetic factors that make the grapevine resilient.
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/pm/soil-salinity-wild-grapevine-defends-itself
-
The AlbLavendel project - 20/11/2023

Blue-violet, fragrant fields like those in Provence may soon become a common sight in the Swabian Alb. As part of the AlbLavendel project, the University of Hohenheim along with the company naturamus GmbH and the German Institutes of Textile and Fibre Research Denkendorf has started to investigate the cultivation of lavender, the production of essential oils and the use of distillation residues for producing textile fibres in the local region.
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/news/swabian-lavender-cultivation-aesthetic-and-sustainable
-
Wasser 3.0: #detect|remove|reuse - 31/10/2023

We all pollute our water with things we use in our everyday lives. In the process, microplastics and micropollutants accumulate in sometimes significant quantities and are difficult to remove. This has increasingly devastating consequences for our health and the environment. Wasser 3.0, a non-profit start-up from Karlsruhe, has declared war on this problem by developing a customisable process to detect, remove and even recycle these pollutants.
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/news/how-sustainably-remove-and-recycle-microplastics-water
-
Climate-neutral wastewater treatment plants thanks to patented real-time analytics - 08/11/2023

The wastewater industry is responsible for global greenhouse gas emissions equivalent to those of global aviation. The start-up Variolytics has found a way to significantly reduce greenhouse gases in wastewater treatment plants using real-time analytics. The patented sensor technology and AI-supported process optimisation offer multiple benefits: in addition to reducing nitrous oxide, the system helps to reduce energy costs and resources.
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/news/using-ai-reduce-greenhouse-gases-wastewater-companies
-
-
-
Press release - 02/11/2023
The Sustainability Innovation Campus (ICN) initiated by the University of Freiburg and the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT), which will begin its work in January 2024, has announced a two-year funding programme for start-up projects. Scientists from the University of Freiburg, KIT and cooperating universities and research institutions are invited to submit their project outlines by 30 November 2023.
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/pm/sustainability-innovation-campus
-
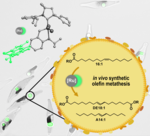
Sustainable binder alternative - 18/12/2023
Plastic is all around us; and unfortunately, it is not going away any time soon. The search for more sustainable solutions is fully underway. However, binders that degrade only with difficulty or not at all are still used to bond natural materials such as wood and straw - not yet truly environmentally friendly. Fraunhofer researchers are working on an insect-inspired wood binder that makes bonded wood products both resistant and biodegradable.
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/news/copied-insects-new-biological-wood-binder-under-development
-
urban BioEconomyLab - 07/12/2023
Baden-Württemberg is leading the way in the transition to a climate-neutral and sustainable economy. One of the projects undertaken is the Fraunhofer IGB’s "urban BioEconomyLab" project which aims to develop a transformation model and living laboratory to find bioeconomic solutions for the sustainable design of cities and municipal industry. What is new is that the IGB takes a systemic approach, focusing on biobased and circular value…
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/news/city-living-laboratory-bioeconomic-sustainable-economic-area
-
Alternative construction materials: mycelium-based materials - 20/12/2023

Most of us see fungi as just food - and possibly pathogens. This is a mistake, because these amazing organisms are capable of much more: they grow on plant residues of all kinds, forming a dense and interconnected structure as they spread. The resulting material can be moulded into desired shapes and be turned into new sustainable and economically attractive products such as leather and polystyrene substitutes or building materials.
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/news/using-fungi-create-sustainable-and-economical-mycelium-based-materials
-
-
-
Dossier - 16/06/2014

Biotechnology opens up numerous opportunities for the food industry. The targeted use of biotechnological methods can help reduce the quantity and number of unhealthy ingredients in foods as well as degrade allergenic substances. Genomic research and targeted breeding also greatly facilitate progress in agriculture. Food biotechnology therefore contributes significantly to saving resources, optimising harvest yields and producing better foods.
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/dossiers/biotechnology-as-a-tool-for-the-production-of-food
-
-
-
Dossier - 14/06/2016
The number of publications and patents that involve the CRISPR/Cas system has been increasing exponentially since the technique was first described a few years ago. The increase in funding for projects involving CRISPR/Cas also demonstrates how powerful this new method is. The targeted modification of genomes (also called gene or genome editing) using CRISPR/Cas is extraordinarily accurate and also has the potential to cure hereditary diseases.
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/dossiers/crisprcas-genome-editing-is-becoming-increasingly-popular
-
-
Dossier - 23/07/2012

Extremophilic bacteria love it hot, sour or salty, toxic substances like heavy metals also do them good and even give them energy. As molecular and systems biology techniques get better and better, industry is also becoming increasingly interested in these exotic organisms. What potential does knowing the biochemistry of extremophilic bacteria have for the pharmaceutical, cosmetics and sanitary articles industries?
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/dossiers/extremophilic-bacteria
-
-
Dossier - 26/03/2012
What is nanobiotechnology what is the difference between nanotechnology and nanobiotechnology and where and what nanobiotechnological research is being carried out in Germany and more particularly in Baden-Württemberg and which applications is it aimed at?
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/dossiers/nanobiotechnology
Website address: https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/search