-
-
-
Diatoms as a biorefinery - 05/05/2023
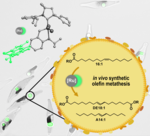
Renewable raw materials that can be used as alternatives to fossil resources already exist. However, to turn them into everyday products, plant oils and other renewable raw materials not only have to be extracted, but often have to undergo complex chemical processing. Researchers at the University of Konstanz have now converted microalgae cells into tiny refineries to produce and upgrade raw materials, creating a supply of sustainable chemicals.
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/news/microalgae-sustainable-chemical-production-mini-factory
-
-
-
-
-
Think Tank FYI: Agriculture 5.0 - 16/02/2023

Climate protection, agriculture and biodiversity are closely intertwined. Agriculture 5.0 provides positive guidance, as the Offenburg University of Applied Sciences has demonstrated: agrophotovoltaics (or agrivoltaics), which is currently in vogue in Germany, can be used to generate solar power on high-yield fields. Biomass strips and biochar remove CO2 from the atmosphere. All this improves soil quality and promotes biodiversity.
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/news/agriculture-50-fighting-climate-crisis-agrophotovoltaics-and-biochar
-
-
-
Project FuTuReS - 12/12/2022

Algae are aquatic organisms that flourish in a huge variety of species. But that's not all: they are also small green mini-factories that can produce all kinds of valuable materials. All they need is water, light, CO2 and a few nutrients that can be recycled from biogas or sewage treatment plants. Researchers have now determined the optimal framework conditions and practicability of process methods for agricultural algae cultivation.
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/news/microalgae-high-quality-products-domestic-agriculture
-
-
-
-
Festo’s high-tech bioreactor - 10/11/2022

In future, algae could be used to produce practically everything that still requires petroleum, including plastics, fuels, medicines and food. Algae are also climate savers par excellence, because they bind ten times more CO2 than terrestrial plants. Festo, a company based in Esslingen, Germany, has developed a high-tech bioreactor that can be used to automatically cultivate the small green biofactories - and that do so a hundred times more…
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/news/valuable-materials-all-kinds-produced-automatically-living-cells
-
-
-
Renaturalised peatlands as carbon dioxide stores - 14/06/2022

All intact peatlands on our planet store twice the amount of CO2 as all forests. Peatlands are indispensable for preventing and mitigating the effects of climate change. The only problem is that 95 percent of Germany's peatlands have been drained, and thus release around 7 percent of Germany’s total CO2 emissions into the atmosphere. Rewetting is therefore imperative for the climate, the environment and biodiversity – and economically…
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/news/peatlands-climate-protection-factor-binding-co2-instead-releasing-it
-
Press release - 06/04/2022
The University of Stuttgart is contributing to innovations for climate protection as part of the EU project "Smart Circular Bridge". An old material is being rediscovered: flax has been with us for thousands of years in the form of clothing, sacks, and robust ship's ropes. Now the plant fibres are experiencing a renaissance and could become the building material of the future.
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/pm/high-tech-bruecke-mit-flachs-gebaut
-
-
-
-
-
Further utilisation of plant residues - 25/11/2021

Biogas plants produce energy-rich gas by fermenting biomass. This process generates both liquid and solid fibrous and particulate fermentation residues. Researchers at the German Institutes of Textile and Fibre Research (DITF) have now managed to create a resistant and water-repellent fibre composite material from solid hop residues that can be used as a veneer to coat wood panels.
https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/articles/news/novel-fibre-composite-made-hop-fermentation-residues
-
Website address: https://www.biooekonomie-bw.de/en/search










